Two of the most popular digital marketing tools are better together.
Two of the most popular tools used by digital marketers today are Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager. Because they are used in conjunction with one another, people are often confused about the differences between them.
Google Analytics is a free web analytics tool that lets you track important metrics for your website like where do your users come from, who are they, and what do they do once on your site. It also provides a user interface for digital marketers to analyze this information through built-in and customizable reports.
Google Tag Manager, by contrast, is not an analytics tool. Google Tag Manager is a tag management system.
A tag is a small snippet JavaScript that sends data from your website to an analytics tool like Google Analytics OR other tools like Facebook, Hotjar or LinkedIn Insights. For instance, this is what the Google Analytics pageview tag looks like in code:
<!-- Global site tag (gtag.js) - Google Analytics -->
<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=UA-XXXXXXXXX-1"></script>
<script>
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag('js', new Date());
gtag('config', 'UA-XXXXXXXXX-1');
</script>
Just like IF THIS THEN THAT makes it easy to trigger integrations based on actions
- IF I leave the house, THEN turn off the lights,
Google Tag Manager makes it easy to trigger tags based on user actions on your site
- IF the user loads a new page THEN fire the Google Analytics pageview tag.
That same snippet of Javascript above, when implemented with Google Tag Manager now looks like this:
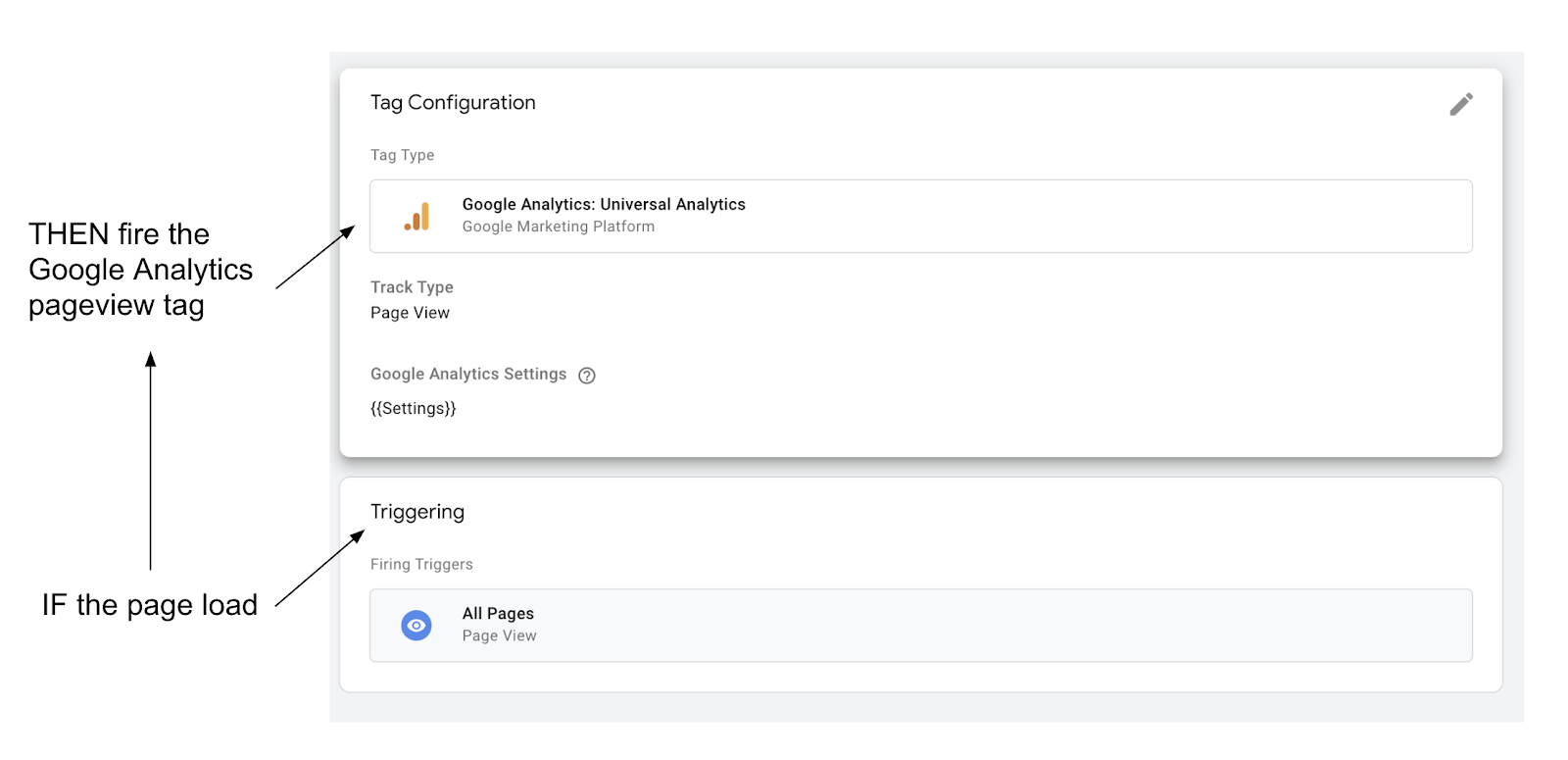
As this demonstrates, you won’t choose between Google Analytics OR Google Tag Manager, you will choose whether or not to use Google Tag Manager to IMPLEMENT to Google Analytics.
Without Google Tag Manager you will have to hardcode Google Analytics directly in your website’s code. So the only part of Analytics that Tag Manager replaces is the hardcoded snippets.
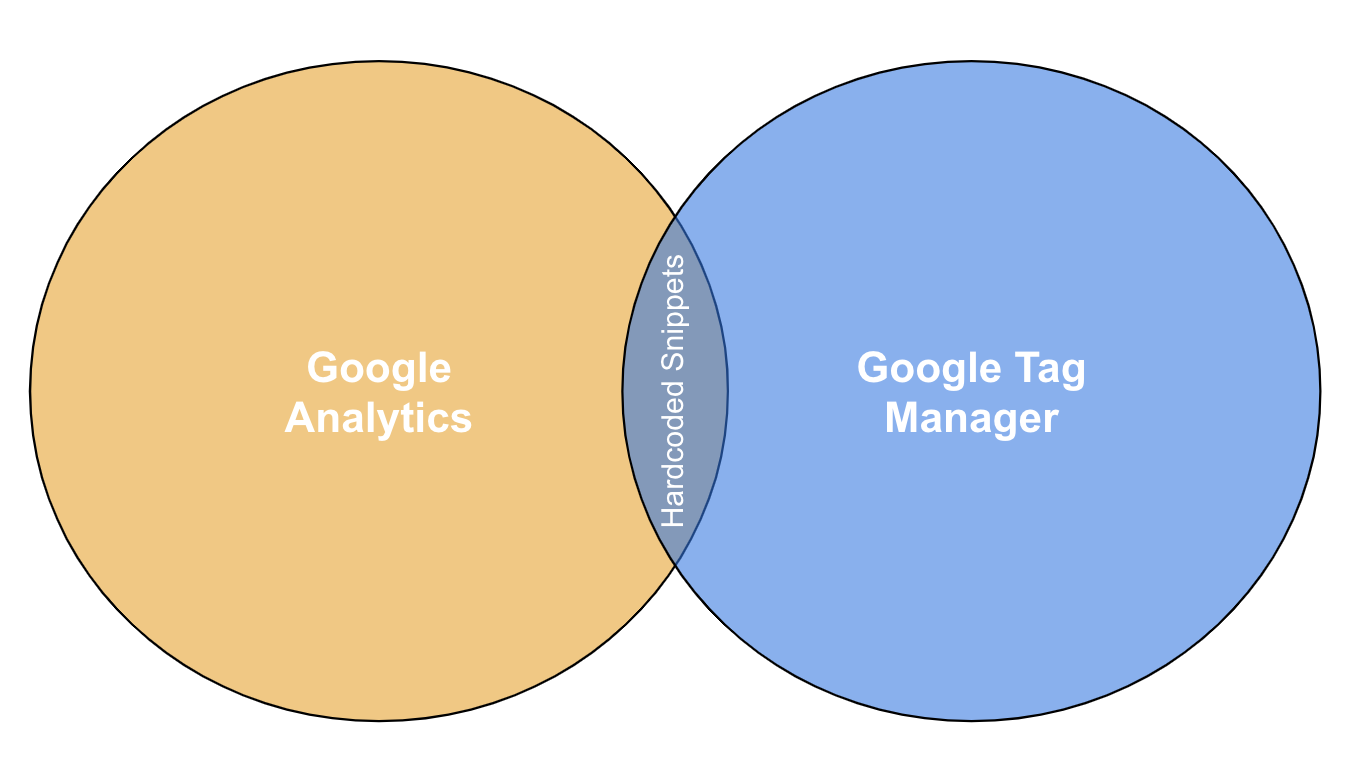
Why Use Tag Manager
Unless you already have many hardcoded Analytics tags you should almost certainly use Tag Manager to implement Analytics. Here’s why.
Dynamic Interactions
While hardcoded Analytics may not be a problem for simple, static webpages, it can cause complications and issues for dynamic websites with lots of user interactions.
For instance, suppose you want to track an Ecommerce Funnel with steps like “add to cart”, “start checkout”, and “payment”. Without Tag Manager, you’ll have to add new Javascript to fire a Google Analytics event for EACH of these steps.
With Tag Manager, you set up your Google Analytics ecommerce events using its simple user-interface. For instance, you could create a trigger based on an Add to Cart button click like so:
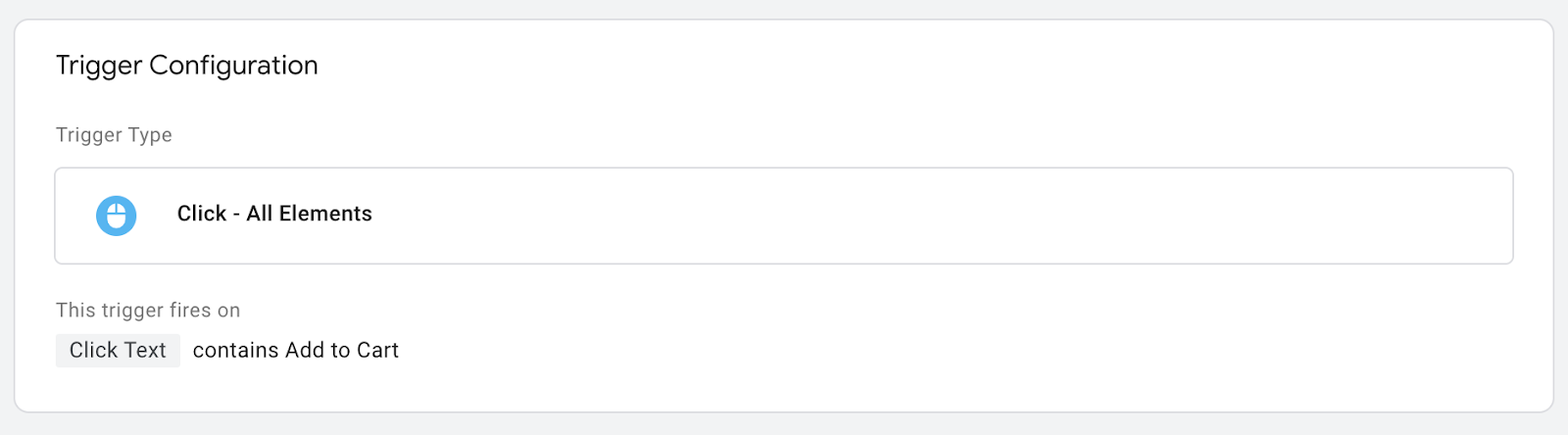
Avoiding Dev Cycles
With hardcoded Analytics, analytics changes are part of the “dev cycle”. Every time you want to make a change to your analytics, to track something new, or change the way an event is recorded, you’ll have to ask the development team to make the changes in code and release the new code to production.
Tag Manager once set up, requires no such coding changes. You can just make the changes you want directly in the Tag Manager user interface.
Tag Manager also provides a simple preview mode that makes it easy to debug changes as you make them without affecting the live site.
Data Consistency Across Tools
Google Tag Manager works with all marketing tools, not just Google Analytics.
Suppose we wanted to track our ecommerce steps in multiple tools like Facebook, Google Ads, and LinkedIn Insights. Without Tag Manager we’ll have to insert new javascript for each tool at each step.
That can easily lead to data discrepancies between the tools, even between related tools like Google Analytics and Google Ads.
However, with Google Tag Manager we can reuse the same trigger we created for our Google Analytics tags for the other tools, ensuring data consistency.
Transparency
With hardcoded Analytics, the source of your analytics will be buried in the code of your website. That makes it very difficult for even coders to track down why a tag fires.
But Tag Manager’s interface makes it clear to all what triggers cause what tags. That makes it easier to update and grow your analytics as you grow your website. It also makes it easier to debug for everyone, including new employees and/or consultants, making it easy to expand your analytics as you expand your team.
Power
While Tag Manager has built-in tags for many tools like Google Analytics, Ads, and Hotjar, it still allows custom tags either through Custom Templates or Custom HTML tags that you can use to cover all possible needs.
That’s because Tag Manager allows you to insert any Javascript you like into your webpage. In other words, anything you can implement with Javascript code directly on your website, you can implement with Tag Manager’s custom tags.
Ready-Made Recipes
There’s an entire community of Tag Manager experts out there. These experts are constantly coming up with new ways to leverage Tag Manager. Furthermore, Tag Manager allows you to export and import containers so these experts (or you) can actually create ready-made recipes that can be imported directly into your containers.
That can be particularly important for organizations that manage multiple, similar websites. You can configure Tag Manager once and simply export it to all of your other sites.
Hybrid Solutions
Finally, you don’t actually have to make a choice between hardcoded Analytics and Tag Manager. If you already have hardcoded Analytics tags in place or use a built-in third-party Analytics plugin like Shopify’s, you can add Tag Manager for new tags, creating a hybrid solution.
That’s because, at the end of the day, both hardcoded Analytics and Tag Manager send the exact same data Analytics. The only difference between the two is how you set it up, with code-level changes or a clean, easy to understand user-interface.
Conclusion
When setting up a new website or revamping your analytics you’ll almost certainly want to use Google Analytics to track your site’s performance. Check out this checklist of best practices for using Google Analytics. Fortunately, Tag Manager makes it easier than ever to set up Google Analytics.
So don’t feel like you have to choose between Google Analytics and Tag Manager. You should, in fact, use both.
Need help collecting all your marketing spend and performance data into automated reports and dashboards? Improvado can help. Click here to learn more.
500+ data sources under one roof to drive business growth. 👇
.png)
 (1).png)
.png)

.png)




 (1).png)

.png)





.png)


.png)
.png)
